Augmented Reality: Where Reality Meets Imagination
“Any sufficiently advanced technology is indistinguishable from magic.” In the context of augmented reality, these words ring particularly true. Not only has it swiftly emerged as a driving force behind transformative marketing campaigns, but it even translates complex computer-generated content into unforgettable brand experiences. Augmented reality is a technology that superimposes digital images on a user’s view of the real world, providing a composite view. In contrast to virtual reality, where a fabricated environment is created, augmented reality offers an interactive experience that seamlessly blends the real world with computer-generated content. Before its modernization, augmented reality (then “virtual fixtures”) compensated for the limited 3D graphics processing power of the time. This groundbreaking approach contributed to bridging the gap between the physical and digital realms with a mix of technology and perception. Looking at the increasing trends for data collection and analysis, the revolutionary advent of AR has fostered an increased understanding of the features of the physical world, making it possible to derive enhanced and accessible insights that can assist in better decision-making at the marketer’s end and offer an immersive product experience to consumers.

Reimagined Marketing Experiences
The digital marketing era brings along constant revolutionary innovations in order to engage their target audience, and augmented reality is no exception to that. It provides customers with immersive, convenient, and personalised experiences. The global market for augmented reality is expected to reach $97 billion by 2028 (Cappasity, October 20), with 80% of consumers interested in using AR for an enhanced shopping experience. A Forbes report anticipates a steady rise in the adoption of high-performance applications like artificial intelligence, virtual reality, and augmented reality, which can prove to be the next disruptor in the field of commercial advertising. With the potential to garner a huge attention market, sectors like retail, fashion, hospitality, entertainment, and healthcare are largely anticipated to lead the way in adopting AR as an effective marketing tool while battling the challenges pertaining to ethical concerns, technical know-how, and customers shifting inch by inch towards trusting augmented reality.
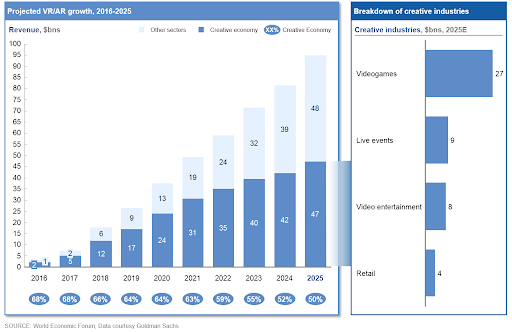
Unlocking the Marketing Potential of AR in Business Campaigns
The integration of marketing with the concept of augmented reality is a prudent experiential marketing strategy to introduce a sense of personal touch to customer experiences. Despite playing a trailblazing role in the marketing space, the implementation of the same is up to the marketer’s discretion. Augmented reality can be put into practice in the following ways:
1. Augmented Branding Material:
As a marketer, it is imperative to ensure enhanced customer experiences to see increased retention rates and evoke positive emotions in a user. Thus, brands look to enhance in-store experiences in order to maintain the offline presence of their respective brands through augmented branding tactics.
Burberry, a popular clothing retailer, employs a beauty mirror using facial recognition technology that allows customers to try on different makeup looks before they buy. The brand’s ‘Beat of the City’ campaign offered a virtual Burberry fashion show in the user’s own city. It has installed touchscreens in its stores that allow customers to explore the brand’s products and collections in AR.
2. Trying Before Buying:
Augmented reality surpasses the limitations of e-commerce by allowing users to try on and physically interact with products like makeup, clothing, and glasses before proceeding with purchases.
The L’Oréal Makeup Genius app, using AR, allows users to see how different beauty accessories would look on their faces. Similarly, IKEA used AR to allow customers to see how different pieces of furniture would look in their homes by simply pointing their phones at a blank space before they made a purchase.
3. Augmented Touring:
Historical and cultural content in varied dialects is integrated with AR to create real-time visual experiences along with real-time simulation practices.
Starbucks leveraged augmented reality to provide customers with access to its rich history and the story of coffee beans through the Starbucks app. Mercedes is another brand that has experimented with AR-based test drives to help buyers experience driving in a virtual environment.
4. Experiential Marketing:
Augmented reality, if used wisely, can strengthen brand image, gathering widespread traction in terms of users and building awareness. It involves promoting a brand while managing to strike an emotional chord with the user.
An ideal example of this application is the Pepsi campaign in a London bus shelter, which attracted users by displaying flying saucers, UFOs, robots, and other objects within the AR window while waiting for a bus. Pepsi has also garnered massive brand awareness through AR-based bottles, music festivals, and scavenger hunts.

AR in Marketing: Pros and Cons
1. Increased brand awareness: The experience offered by AR appeals greatly to the emotional sentiments of users. It ensures effective brand promotions and a wider market reach. Augmented reality can increase brand awareness by up to 200% if used constructively.
2. Boost Sales: Augmented reality marketing taps into the psyche of Gen Z and persuades the user to purchase the product/avail the service. Using it can increase sales by up to 30% if leveraged to its optimum potential.
3. Enhanced customer experience: Adopting augmented reality leads to a steady rise in conversion rates and a hesitation-free commitment to the product, leading to a favourable buying decision.
4. Fall in returns: AR-based tech advertisements generate an informed user base that has an established connection with a brand and possesses all relevant information about a product in terms of experience, features, and the cost involved. This induces greater customer retention and a fall in returns.
5. Overcoming e-commerce barriers: With the advent of AR-based marketing, customers can experience products and gain an enriching experiential advantage. Memory encoding happens to be 70% higher with AR experiences as compared to regular 2D advertisements.
Augmented reality is a powerful tool for businesses to enhance customer attraction and drive sales. However, cost constraints and limited adoption rates are concerning. Additionally, accessibility issues and the absence of necessary digital resources hinder widespread acceptance. Privacy concerns arise due to the collection of private customer data to track user behaviour, necessitating businesses to raise awareness and educate consumers.
Conclusion
Augmented reality and virtual reality have vast untapped potential to revolutionize the customer experience. With rising expectations and dynamic consumer behaviour, it becomes imperative for businesses to align themselves with existing marketing practices. Augmented reality has opened doors for businesses to reinvent product interactions and connect with their audience on a more personal level. Considering AR’s malleability to be employed in nearly every industry, the number of mobile AR users is expected to touch 800 million and grow to 1.73 billion by 2024, taking the annual growth rate of augmented reality to 76% in India (Sifted, 2022).
It stands to be one of the most promising strategies for businesses in the coming years. The use of AR will help forward-looking brands upgrade their customer experiences to see improved opportunities and sales. Augmented reality has gone from pipe dream to reality in just over a century. Given the unlimited opportunities, will the technology be able to leverage and unlock the envisioned marketing potential?
References
- Team, D. C. (2022). Augmented Reality Marketing – A Comprehensive Guide. From Deskera Blog.
- Panel, E. (2020, September 4). 10 Industries Likely To Benefit From AR/VR Marketing. From Forbes.
- Kakovkina, V. (2022). Augmented Reality and marketing: How and why to use AR marketing. From VistaCreate.
- Thakkar, S. (2021, April 5). How Augmented Reality Is Changing The World Of Marketing For Brands. By Inc42 Media.
- Augmented Reality – The Past, The Present and The Future. (2023, June 13). From The Interaction Design Foundation.
- Hayes, A. (2023). Augmented Reality (AR) Defined, With Examples and Uses. From Investopedia.
- Sifted. (2022). The future of augmented reality in four charts. From Sifted.
- Getter, P. (2023, January 31). What Is The Future Of Marketing In 2023? From Forbes.
- Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality. (n.d.). World Economic Forum.
- Campbell, C. (2019). How to transform retail for the future with augmented reality. www.ey.com.
- Statista, “Number of Augmented Reality (AR) Users Worldwide from 2016 to 2024 (in Millions)”
- Forrester, “Augmented Reality in Retail: The Next Frontier in Customer Engagement”
- ARtillery Intelligence, “The State of AR in Retail 2022”


Quite insightful ! A whole new world of AR nicely articulated. Best wishes
A very well written and informative blog! Keep up the good work!!
An insightful content article very useful.
Very well-articulated! Great work!!