Introduction
The Chinese economy is currently experiencing a significant slowdown, with the real estate sector at the epicenter of the crisis. The collapse of Evergrande, the world’s most indebted property developer, in August 2023 sent shockwaves through the global economy, and its ripple effects are now being felt throughout the Chinese economy.
Consumers and real estate investors have lost confidence in the sector, and aggregate demand and housing prices are plummeting. As a result, the unemployment rate has risen to 21%, and deflation is looming. Economists warn that the Chinese economy is on the brink of recession.
The Growth Engine that is Running Out of Gas
To better understand the current situation, it is important to look back at the past 30 years of Chinese economic growth. The country has relied heavily on debt-fueled investment in infrastructure to boost its growth rate. This approach was successful in creating jobs and building long-term assets, but it has also left the Chinese economy highly leveraged and vulnerable to shocks.
In recent years, the Chinese working-age population has declined significantly, and the COVID-19 pandemic has exacerbated the slowdown in economic growth. Moreover, the Chinese government has not provided stimulus checks to its citizens, which has further dampened household spending.
As a result of these factors, the Chinese economic engine is running out of gas. The real estate crisis is a symptom of the underlying problems in the Chinese economy, which include an aging population, high debt levels, and a lack of domestic demand.
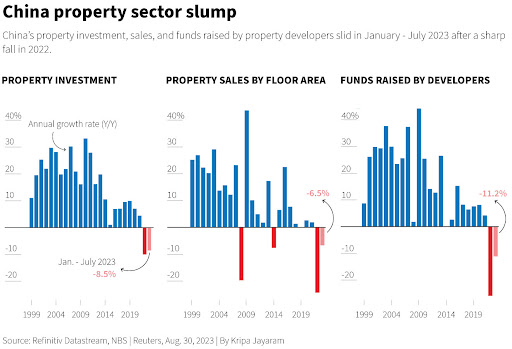
The graph above shows the property slump that has occurred in China. Rather than increasing their consumption expenditure people have spent their money on investments especially real estate but once the real estate companies started defaulting on their loans, it eroded the trust of the people leading to a severe decrease in the demand of real estate.
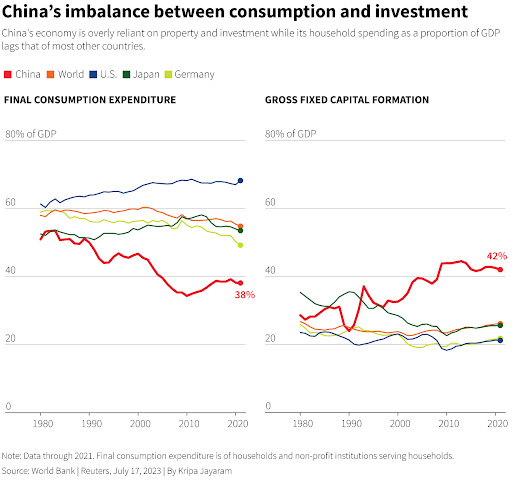
The above graph highlights a major problem that is currently being faced by China. Unlike, it`s western counterparts which provided stimulus checks during Covid lockdowns which resulted in a buying spree and increase in consumption expenditure once the lockdown was over, no such phenomenon was visible in China as neither the government had provided any stimulus checks nor the people were interested in increasing their consumption expenditure leading to an economic slowdown.
What is the Central Bank doing?
The Chinese government is undertaking a number of monetary efforts to keep the economy afloat and safeguard it from the real estate crisis. One of the key measures is to cut interest rates. This makes it cheaper for businesses to borrow money and invest, which can boost economic growth. However, there are a number of potential challenges that the Chinese economy could face following the interest cut. In the short term, the interest cut may appear to revive consumer confidence and boost investment. However, in the long run, it could lead to higher inflation. This is because when interest rates are low, there is more money available in the economy, which can drive up prices. If inflation becomes too high, the central bank may be forced to raise interest rates again, which could slow down economic growth. There is also a lack of concrete evidence to suggest that cutting the medium-term lending facility (MLF) rate by 15 basis points and the reverse repo rate by 10 basis points will be effective in supporting the Chinese economy. More research is needed to understand the full impact of these measures.
Trade War With US
While the impact of the Chinese economic slowdown on the US economy has been modest so far, economists warn that a prolonged slowdown could have a significant impact on global supply chains and US businesses. Reduced household spending in China is likely to lead to a decline in demand for imported goods, which could hurt American MNCs that have a significant presence in the Chinese market. Additionally, a prolonged slowdown in the Chinese economy could disrupt global supply chains, making it more difficult and expensive for US businesses to obtain the goods and materials they need.The spillover effects of the Chinese economic slowdown are likely to be felt most acutely by nations that are heavily dependent on the Chinese economy. However, the slowdown could also have a significant impact on the US economy, particularly if it leads to disruptions in global supply chains.
Conclusion
The Chinese economy is heavily reliant on the real estate sector. The recent crisis in this sector has had a significant impact on the overall economy. It is important for the Chinese government to develop a strategy to support the real estate sector and other key sectors of the economy.Given the lack of clarity on which sectors to invest in, the Chinese authorities risk providing stimulus to the wrong industries, which could further distort the economy and delay its recovery.
References
- Reuters. (2023, September 1). Why is China’s economy slowing down and could it get worse?
- How China’s slowdown could hit Washington and Wall Street. (2023, September 5)
- Yao, K. (2022, July 15). China’s economy brakes sharply in Q2, global risks darken outlook. Reuters
- Gao, L., & Woo, R. (2023, September 15). China’s property slump worsens, clouding recovery prospects. Reuters
AUTHOR:
Rahul Dey
[email protected]
B.A. (H) Economics, 3rd year
Shyam Lal College (E), University of Delhi

Recent Comments